Network Security Assessment
Summary
The purpose of this whitepaper is to illustrate the most common mistakes which take place in IT security management, and provide effective measures against them. It gives no narration of pioneer-level technologies but the very practical and useful solution to Threat Identification.
Introduction
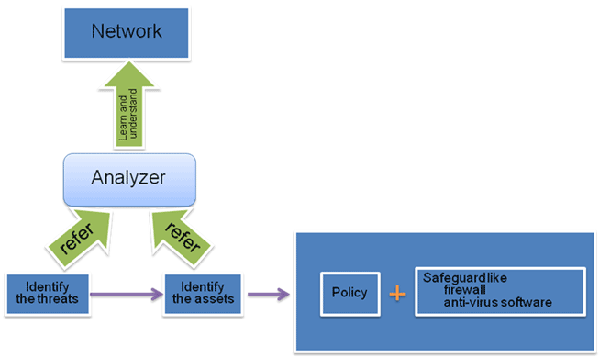
The misbehaviors in security management are always "did not do the right thing" or "did not do it correctly". But trace back to the root, the main reason appears to be a single expression - not enough understanding about your system. Actually good security policies are defined based on proper Threat Identification, Asset Identification at the first place, while the identification process requires a clear vision of how IT system works. Protocol Analysis is a technology used in tracing and decoding network traffics, thus offer you a vivid picture of all the information flow running in your network, so that you can refer is and determine threats and assets, and set up security policies.
Challenge
Based on the report from Verizon Business in 2008 - 285 million times of hacking records over 90 sorts of vulnerabilities - the organizations failed to defend them all because of some stupid misbehaviors, which can be divided into 10 categories. Some of them can be easily defended but others are not that easy - they require more inspection to determine what to do next.
No proper ACL configured
This is a very simple method to protect your system by constrain the accessibility - allow only those who should be able to access your system through network.
For Example, you have a customer who needs to fetch the data from server remotely through VPN connection. You should use ACL to make sure he/she can access only the data server so that even there are hackers successfully hacked in via the open VPN connection, it is not possible for them to access any other resource than the data server.
But why no proper ACL configured?
It is actually very easy to configure ACLs by imputing commands. But this is not really the key part of a proper ACL implementation. It is the policy who upsets the administrators. How do you develop a proper policy to rule the traffic? Which department can/can't directly access the financial department? You can hardly do this without knowing the business diagram in your network. But how do you suppose to know? Ask the CEO/CIO if there is any application running directly between these departments? I don't think so.
No countermeasure or policy against unauthorized/insecure remote access and administration tools.
Hackers are use to take advantage of remote administration tools to get through the Access Control mechanism of network security systems. Unauthorized access is always one of the most common security breaches based on the research of CSI Computer Crime & Security Survey, and security breach happens again and again because no countermeasure against remote access?
Why there is no proper countermeasure even they've noticed the urgent need for this?
In fact, people know exactly what to do to protect their system but how to do is the real barrier in the way to secure. The most difficult part of guarding your system from unauthorized access is to find out where such things like VNC, PCAnywhere, or SSH is available and happening. How do you collect information about these potential threats? How could you know if individuals secretly installed a VNC service on host machine? Do you ask all the staff by broadcast? Or check the hosts one by one? I am not sure about it.
Did not block the unnecessary external traffic
One of the tricks the malwares use frequently is to install backdoors or Shell on the servers so they can login to the server firstly and then try to hack in your network by establishing connections from the server. A very good method to avoid such kind of threat is to block the unnecessary traffic.
For example, a Web server shall not send telnet traffic to anyone within or without the network in a general sense; a Log server shall not initiate any connection towards any peer. So only the necessary traffic should be allowed and other traffic should be blocked by default.
But, block or not, it is a question
The decision-making process is not that easy like telling the black and white. You need to know the characteristic of the traffic (e.g. IP source/destination/ports); you also need to know which of them is vital to the productivity which is routine and which is unwanted. But how to get these information?
Did not know where the second level branch of Private Data was stored.
Private Data such as customer information, software codes, agreement documents are well protected in most cases of security incidents, but the data leakage happened however. It is frustrating - why? Is the safeguard not strong enough? How did they bypass the firewall? I haven't see any log indicating the data was once been accessed, how did this happen?
The answer is beyond all expectations - the source of data leakage is not from the data server themselves, but the backup storage, and other places which would hold this information. Unfortunately, such sorts of place are free of proper protection in most cases.
Why there's no proper protection for them?
It is not these places holding sensitive data have been deemed as non-significant, but nobody knows where the sensitive data flows to thus no protection provided. To inspect where the assets goes and come in the information flow is the key method of find out where are the points to be protected.

All the aforementioned items are brought up by the same challenge - did not understand your network thus no security inspection can be conducted - thereupon, no proper protection can be carried out because failed to know what to be protected, and from what.
Opportunity
There are several practical and mature technologies in the market:
Sniffing technology
This technology allows users to accept all traffic no matter whether they are heading to whom. Sniffing tech will also be able to reconstruct the traffic, decode them and translate them it to human readable information.
SPAN/Port mirroring
It is a matured tech which is widely used in IDS/IPS systems. As we know not all the network traffic goes through a single path, sniff at a single point will not provide you the image of your entire network. However, SPAN is the most practical way to solve this problem in the modem world - it allows you to copy traffic from multiple switch port and send to the specified port for analyzing.
A combination of the above two technologies gives a perfect way of learning and understanding the network, thus enhance the link between the analyzer and the network.
Colasoft provide products and services to make the analyzer to know the network better, and offer statistics to support their suggestions to decision makers. And in the aspect of evaluation and review works, Colasoft offers products to refer and help the CSO or Security Analyst define the policies.
Solution
Colasoft Capsa performs real-time packet capturing, 24/7 network monitoring, advanced protocol analyzing, in-depth packet decoding, and automatic expert diagnosing. It allows you to get a clear view of the complex network, conduct packet level analysis.
Deploy Colasoft Capsa to monitor key sections of your network will strengthen the link between the Analyzer and the network by offer statistics and virtualized graphs.
It helps you inspect security issues by:
- Identify the characteristics of unwanted traffic
- Trace where the information asset goes
- Detect where the unknown threats might be (e.g. unauthorized VNC server)
- And give information about other vulnerabilities in your network






No comments